In case you are a great expert in working with Git, then you would know that how necessary is to set up SSH authentication. Are you excited to learn how to generate Git SSH key and SSH authentication? Then, this tutorial is the best option for you.
From here, you will understand that SSH authentication is one of two ways of logging into your Git remote repository and pushing modifications to it. In this tutorial, we are explaining more about how you can generate SSH keys for Git on Linux, or on Windows, or on Mac. Along with that, you should have some knowledge of Git Commands to check the Git installation version using the command line.
- What is an SSH KEY?
- How to Create an SSH Key?
- Checking PC’s SSH Keys
- Generate a new SSH key
- How to Generate SSH keys for Git authorization
- Setup SSH authentication on Git
- Copy SSH keys to your Git server
- Push Changes to Git through SSH
Note: If you are using Github, follow this tutorial to setup SSH keys on Github
What is an SSH KEY?
The definition of an SSH key is an access credential for the SSH (secure shell) network protocol. For remote communication between machines on an unsecured open network, we use this authenticated and encrypted secure network protocol. Also, SSH is utilized for remote file transfer, network management, and remote operating system access. The SSH acronym is also utilized to specify a set of tools used to communicate with the SSH protocol.
- How To Setup SSH Keys on GitHub | How to Generate SSH Keys Windows & Linux?
- How To Clone a Git Repository | Clone a Git Repository with Command Line & Sourcetree
- How To Change Git Remote Origin | What is Git Remote? | Git Remote Add Origin
How to Create an SSH Key?
SSH keys are created using a key generation tool. The generation of SSH keys can be through a public key cryptographic algorithm, the most common being RSA or DSA. At a very high-level SSH keys are created via a mathematical formula that uses 2 prime numbers and a random seed variable to output the public and private keys. This is a one-way formula that assures the public key can be obtained from the private key but the private key cannot be obtained from the public key.
Checking PC’s SSH Keys
You can check your PC’s SSH Keys by following the command below.
ls -al ~/.ssh
By typing the above command, you can see your SSH keys easily. The filename of the public key is one of the following by default:
id_ecdsa.pub id_ed25519.pub id_rsa.pub
Generate a new SSH key
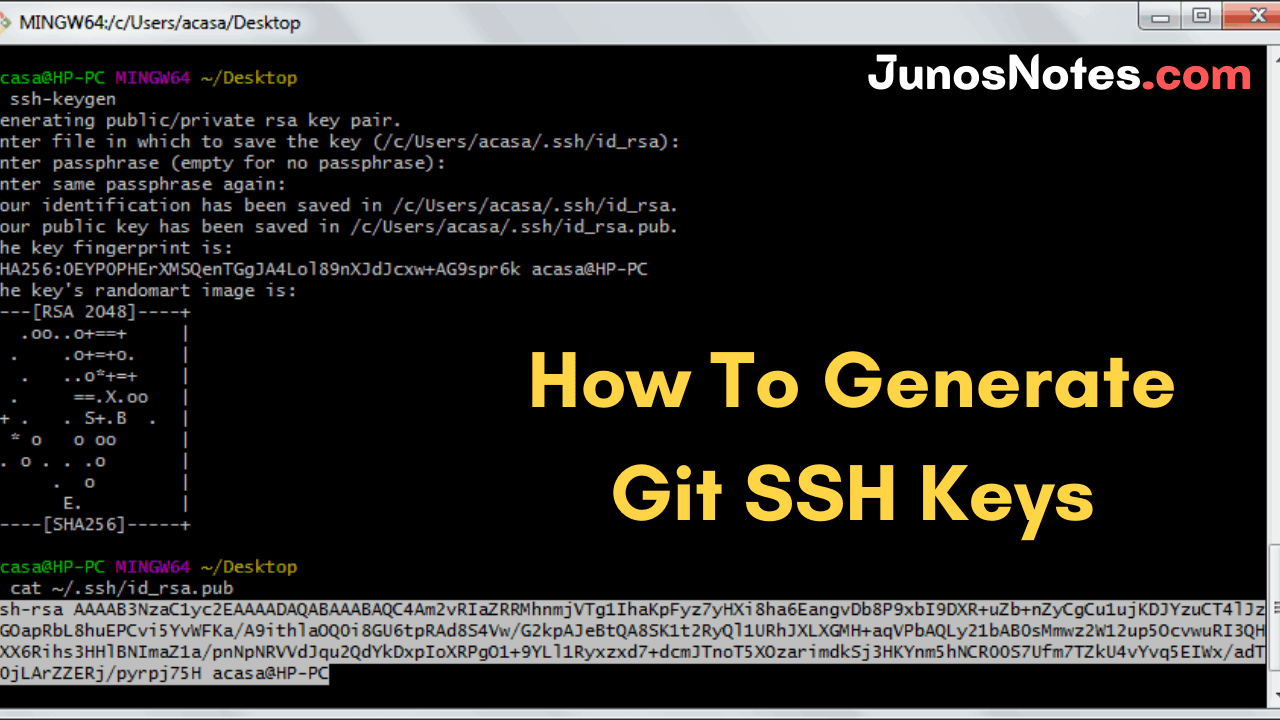
If you don’t have an SSH key, first, you should create it. Later, please follow the step-by-step guide on how to generate a new SSH key.
Type the command below, using your GitHub’s account email:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "[your github's email]"
After running this command, you will be offered to set the SSH key path, but we advise you to use its default value by pressing the “Enter” button.
Enter a file in which to save the key (/Users/you/.ssh/id_rsa): [Press enter]
After that, it will allow you to insert a passphrase to protect your SSH key.
> Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): [Type a passphrase] > Enter same passphrase again: [Type passphrase again]
Read More on Git:
How to Generate SSH keys for Git authorization
This tutorial is all about generating SSK Keys on various platforms like Windows, Mac, Linux, etc. If you poor at this concept then check out how to do it by following the steps given here:
Generate SSH Keys on Linux
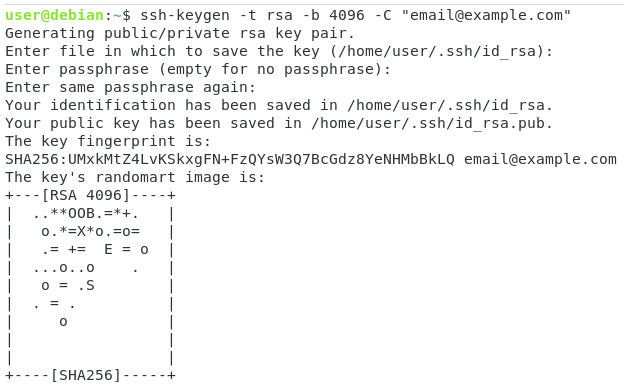
In order to generate SSH keys for your Git repository, use the “ssh-keygen” command and specify the encryption algorithm that you want to use.
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "email@example.com"
Note that it is recommended to generate your SSH keys in the “.ssh” directory of your home directory.
When using the ssh-keygen utility, you will be prompted with multiple questions.
First, you will be asked to provide the filename for your key as well as the passphrase.
For the filename, you usually want to leave the default options and simply press Enter.
For the passphrase, we won’t bother choosing a passphrase for this tutorial.
Even if it includes an extra layer of security for your Git repository, you will be prompted with the passphrase every time that you want to perform an operation on the repository.
The ssh-keygen utility created two files for you :
- id_rsa: this is the private key of your SSH key pair, you should not share this key with anybody.
- id_rsa.pub: this is the public key of your SSH key pair, this is the key that you will copy to your server in order to connect to it seamlessly.
Generate Git SSH Keys on Mac
Just take a look at the below provided five main steps and follow them carefully to generate SSH keys for git:
- Start the terminal
- Navigate to your home directory by typing: cd ~/
- Now, perform the following command: ssh-keygen -t rsa (when prompted, enter a password, the key name can stay the same)
- Open the file you’ve just created ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub with your favorite text editor, and copy contents to your Git repository’s keys field (GitHub, beanstalk, or any other repository provider), under your account.
- Make sure that you don’t copy any whitespace while copying the public key’s content (id_rsa.pub).
Generate SSH keys for Git on Windows
In order to generate SSH keys for Git on Windows, you have to enable the OpenSSH commands using the “Add-WindowsCapability” command.
$ Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Client* Path : Online : True RestartNeeded : False
Note: You have to be an administrator to enable OpenSSH on your computer.
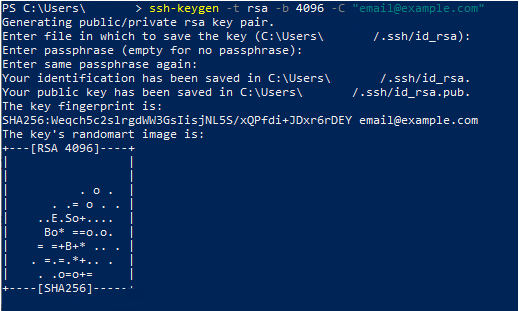
Now that OpenSSH is enabled and configured on Windows, simply use the “ssh-keygen” command in order to generate your SSH keys.
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "email@example.com"
By default, you will be prompted to provide a public key filename as well as a passphrase.
You can leave those options empty: by default, your key-pair will be named “id_rsa” (or “id_rsa.pub” for the public key).
When it comes to the passphrase, it provides more security to add one but you will be asked to provide it on every SSH authentication.
As you can see, your SSH keys for Git are located in the “.ssh” directory of your user home.
The ssh-keygen utility created two files for you :
- id_rsa: this is the private key of your SSH key pair, you should not share this key with anybody.
- id_rsa.pub: this is the public key of your SSH key pair, this is the key that you will copy to your server in order to connect to it seamlessly.
Setup SSH authentication on Git
Now that your SSH keys are generated for Git, it is time to add them to your remote Git repository in order to push changes.
In order to setup SSH authentication on the server, you will have to copy the content of the public key to the “authorized_keys” file of the server.
Copy SSH keys to your Git server
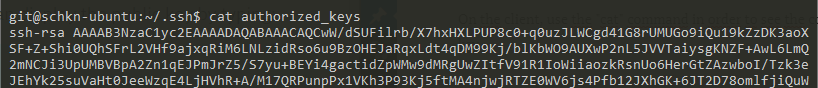
On the client, use the “cat” command in order to see the content of the public key.
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
Copy the output of your cat command, and paste it into the “authorized_keys” file of your server (or remote repository).
$ sudo vi /home/git/.ssh/authorized_keys
Alternatively, if you don’t want to copy and paste the content of your public key, you can use the “ssh-copy-id” command.
This command will simply take the content of your “.ssh” directory and add the relevant public keys to the “authorized_keys” file of the server.
$ ssh-copy-id <user>@<remote>
Push Changes to Git through SSH
Now that your keys are correctly configured for Git, you should be able to pull and push modifications to your Git repository.
Head over to the directory where your project files are stored.
$ cd /home/myproject
If you don’t have a Git repository, initialize one using the “git init” command.
$ git init Initialized empty Git repository in /home/user/myproject/.git/
If there is already a “.git” file in your directory, it means that there is already a repository initialized.
Note: To get the content from your existing Git repository, use the “git clone” command.
Now that your Git repository is correctly configured, add the remote repository using the “git remote add” command.
$ git remote add origin git@<server_ip>:<path_to_git_repository>
On the server, if the “project.git” file (i.e the repository root) is located directly on the git user home directory, you would write
$ git remote add origin git@8.8.8.8:project.git
After adding your remote, make sure that your modifications are effective by running the “git remote -v” command.
$ git remote -v origin git@8.8.8.8:project.git (fetch) origin git@8.8.8.8:project.git (push)
Great!
Let’s now try to add some files in order to test if files can be pushed to your remote repository.
Create a README file using the “touch” command.
$ touch README
Add the files using the “git add” command and commit them using the “git commit” command.
$ git add . $ git commit -m "This is the first commit of this repository"
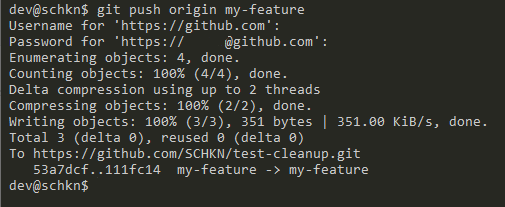
Finally, push your modifications: the push operation should not require any password using the SSH method.
$ git push
Now, you have correctly configured SSH key-based authentication for your Git repository.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how you can generate SSH keys for Git easily using the ssh-keygen utility.
You learned that the same utility is used on Linux and on Windows. The directories used in order to store the keys are also the same.