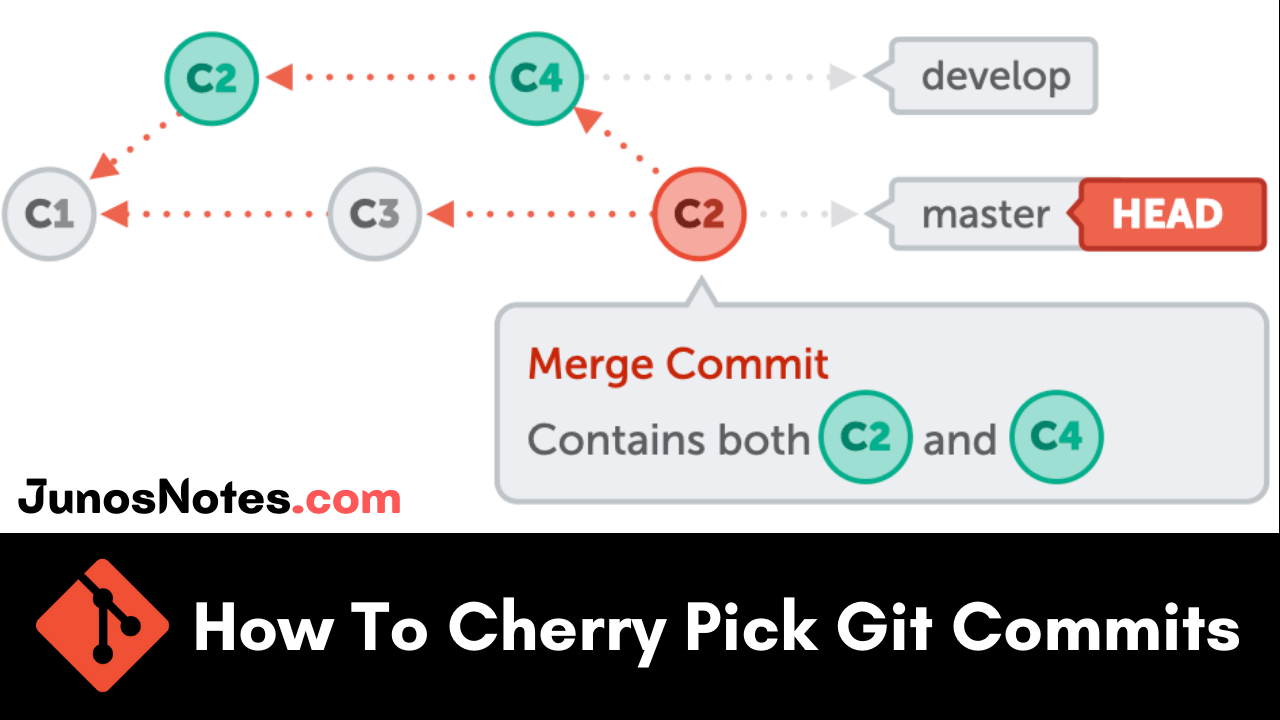
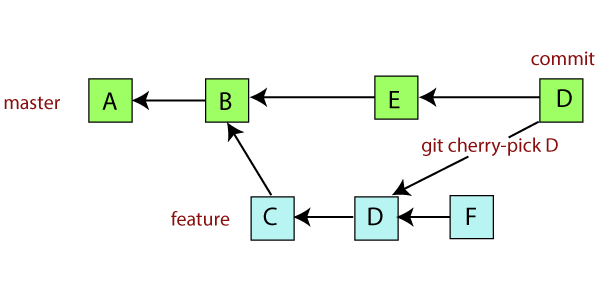
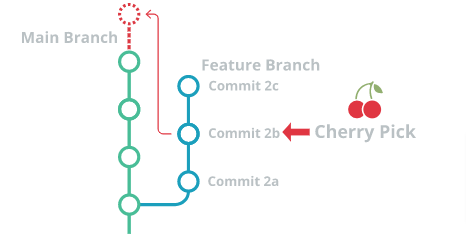
If you are working with Git, you may require to add some specific changes to your current branch. For instance, if you require to include a particular commit located on another branch than your current branch,. To perform this case make use of the required git commands ie., git cherry pick.
It is one of the most useful commands in Git and also it does not change your current Git history rather it adds commits to it. In this tutorial, we will be explaining more about Git Cherry Pick commit and how you can use the Git cherry-pick command for including specific changes to your current branch.
- Git Cherry-pick
- How to use git cherry-pick?
- How do I cherry pick a commit in Git?
- How to Cherry Pick a Commit?
- Cherry-pick using Git commit hash
- Cherry-pick from another branch
- Cherry-pick multiple Git commits
- Cherry-pick with original commit reference
- Change commit message when cherry-picking
- Resolving cherry-pick conflicts
Git Cherry-pick
Git cherry-picking refers to applying some commit from one branch into another branch. If you did any error and performed a change into the wrong branch, then you shouldn’t merge the whole branch. You can revert the commit and apply it to another branch.
The principal objective of a cherry-pick is to apply the changes proposed by some current commit. Cherry-pick is a helpful tool, but always it is not a good option. It is in contrast with different ways such as merge and rebase command.
Do Refer: How To Clear Git Cache
How to use git cherry-pick?
If you want to allow the “cherry-pick” only the commits you want from another branch then Git’s cherry-pick command is useful for you. The following steps are very important to understand how to use git cheery pick:
- Pull down the branch locally. Use your git GUI or pull it down on the command line, whatever you’d like.
- Get back into the branch you’re merging into. You’ll likely do this by running
git checkout master. - Find the commits you want to pull into your branch. Go to either the git log or the GitHub UI and grab the unique commit hashes for each of the commits that you want.
- “Cherry pick” the commits you want into this branch. Run this command:
git cherry-pick super-long-hash-here. That will pull just this commit into your current branch. - Push up this branch like normal.
git push origin master
How do I cherry pick a commit in Git?
In Git, the cherry pick command drives changes from a target commit and puts them on the HEAD of the currently checked out branch.
- How To Undo Last Git Commit | Process of Undoing the Last Commit in Git
- How To Create and Apply Git Patch Files | Creating & Applying Git Patch Files with Different Git Commands
- How To Create a Git Branch | Learn Git Create New Branch from Current Branch
From here, you can either continue working with these changes in your working directory or you can directly commit the changes onto the new branch.
How to Cherry Pick a Commit?
Cherry-pick using Git commit hash
The easiest way to cherry-pick a commit is to use the “cherry-pick” command with the commit hash.
$ git cherry-pick <hash>
In order to cherry-pick changes, you will need to identify your commit hashes.
In order to see the commit hashes for your current branch, simply run the “git log” command with the “–oneline” option in order to make it more readable.
$ git log --oneline 45ab1a8 (HEAD -> branch2) added gitignore 808b598 (branch) Initial commit
By default, the log command will display the commits from the history beginning until the top of your current branch.
As a consequence, you may not see commits that are not related to your current branch timeline.
If you want to see commits related to a specific branch, specify the branch name when running the “git log” command.
$ git log --oneline master 93ae442 (master) committed changes 44ee0d4 added gitignore 808b598 (branch) Initial commit
As you can see, one additional commit was displayed: you can now use this hash in order to cherry-pick your commit.
$ git cherry-pick 93ae442 [master 299a73d] added file Date: Wed Nov 20 16:04:52 2019 -0500 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 file.txt
Great!
You have successfully cherry-picked your commit.
Cherry-pick from another branch
In order to pick commits from another branch, you need to list commits that were performed on this other branch using the “git log” command.
$ git log --oneline <branch>
Let’s say for example that I want to cherry-pick a commit from the feature branch.
$ git log --oneline feature 93ae442 (master) Feature 1 44ee0d4 Feature 2 808b598 (branch) Initial commit
Now, you can go to the branch where you want the commit to be cherry-picked, let’s call it “master” in this case.
$ git checkout master $ git cherry-pick 93ae442 [master 299a73d] added file Date: Wed Nov 20 16:04:52 2019 -0500 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 file.txt
Great!
You successfully cherry-picked commits from another branch into your main branch.
Cherry-pick multiple Git commits
In some cases, you may want to cherry-pick multiple commits at once.
Luckily for you, this option is available since Git 1.7.2.
Since Git 1.7.2, you can cherry-pick a range of commits by using the dot notation.
$ git cherry-pick A..B
Note that using this command, commit A will NOT be included in the cherry-pick.
In order to include commit A, you can use this syntax
$ git cherry-pick A^..B
For example, back to the “master” branch, let’s try to cherry-pick two commits into the feature branch.
$ git checkout master $ git log --oneline feature 481981f (feature) file 4 6653c90 file3 $ git cherry-pick 6653c90^..481981f [master 04fbbcf] file3 Date: Wed Nov 20 16:20:23 2019 -0500 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 file3 [master f3ecc5a] file 4 Date: Wed Nov 20 16:20:36 2019 -0500 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 file4
Note that the commits need to be placed into the correct order: commit A needs to be older than commit B otherwise the command will fail silently.
Cherry-pick with original commit reference
In some cases, you may want to keep a reference to the original commit when performing a cherry-pick.
When you are performing a regular cherry-pick, you will get a new commit hash but the commit message will be the same.
However, there is a way to append the origin of a cherry-pick to the commit message: by using the cherry-pick with the “-x” option.
$ git cherry-pick -x <commit>
For example, let’s say that I cherry-picked one commit from the master branch into my “branch2” branch.
$ git cherry-pick -x ed5d4c4
Now when inspecting the commit list, you can pay attention to the commit name.
$ git log
commit de05030c3c03def40c8fa8f23e5283a7b2eaab6a (HEAD -> master)
Author: Antoine <test@gmail.com>
Date: Wed Nov 20 16:06:10 2019 -0500
added file 2
(cherry picked from commit ed5d4c45dda6a6671df7d8bfc63e293ef1de23fa)
As you can see, the commit has the original commit message but it also has an informational message from the original commit
$ (cherry picked from commit <hash>)
This option can be quite handy when you want to track cherry picks done on the branch.
If you don’t specify the “-x”, you won’t be able to tell if the commit was cherry-picked in the past.
Change commit message when cherry-picking
Cherry-picking commits is very useful in order to reuse some existing work.
However, in some branches, the commit may be useful for different reasons.
As a consequence, you may want to change the commit message when cherry-picking.
To change the commit message when cherry-picking, use “git cherry-pick” with the “-e” option.
$ git cherry-pick -e <hash>
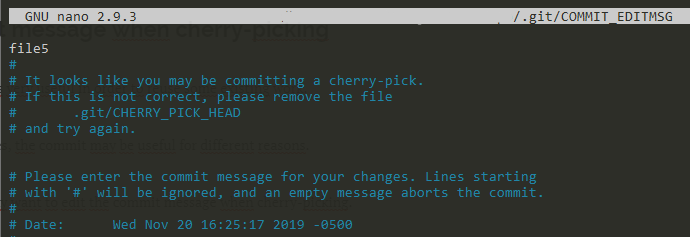
As illustrated in this example, your default editor will open and it will let you change the commit message.
When you are satisfied with the edits, save your file and your commit message should be saved successfully.
[master 1aac0e2] file5 Date: Wed Nov 20 16:25:17 2019 -0500 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 file5
Resolving cherry-pick conflicts
In some cases, you may run into cherry-pick conflicts when trying to cherry-pick your commits with the current branch.
$ git cherry-pick 93ae442 error: could not apply 93ae442... committed changes hint: after resolving the conflicts, mark the corrected paths hint: with 'git add <paths>' or 'git rm <paths>' hint: and commit the result with 'git commit'
This error is happening because Git is trying to merge the content of the cherry-picked commit with your current branch.
However, as in a merge operation, the content merging can fail and you will have to solve the conflicts by yourself.
In order to fix the issues, first, take a look at the status of your working directory and staging area.
$ git status
On branch branch2
You are currently cherry-picking commit 93ae442.
(fix conflicts and run "git cherry-pick --continue")
(use "git cherry-pick --abort" to cancel the cherry-pick operation)
Changes to be committed:
new file: index.js
new file: script.js
Unmerged paths:
(use "git add <file>..." to mark resolution)
both modified: .gitignore
As you can see, the status command states that “you are currently cherry-picking commit 93ae442“.
The files to be solved are located in the “unmerged paths” section. In order to solve the cherry-pick conflict, edit the file and modify the file until you are satisfied with the modifications.
$ nano .gitignore (Previous content) <<<<<<< HEAD ======= *.conf >>>>>>> 93ae442... committed changes (After conflict modification) *.conf
When conflicts are solved, add the files to your staging area and continue the cherry-pick process.
$ git add . $ git cherry-pick --continue
The last command will open your current editor in order to add a message to your current operation.
When you are done, save your changes and your changes should be merged.
[branch2 bd8763f] Fixed conflicts on cherry-pick Date: Wed Nov 20 12:56:50 2019 -0500 3 files changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 index.js create mode 100644 script.js
Great! You successfully resolved cherry pick conflicts on your current branch.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned more about the git cherry-pick command and how it can be used in many ways to merge specific commits into your current working branch.