We all know how important to add many files into a git repository for developing the project. But developers should realize and work on deleting unused files on git. Always, delete files on git is so confusing as it is a big question mark to delete them from my repository or delete them from the filesystem?
Also, Have a look at the Git Commands for gaining enough knowledge & practice on Git.
To clear your confusion, we have come up with this new Git Tutorial on How to Delete File on Git. Here, we have explained completely how you can easily delete files on Git, whether it is only from your Git repository or from the filesystem. Let’s dive into it without any further do.
- The git rm Command
- Delete Files using git rm
- Removing Multiple Files
- Delete Files Recursively on Git
- Delete Files From Git Repository Only
- Delete Files From Git History
The git rm Command
Whenever you are planning to delete or remove a file or multiple files from a git repository, then this command ie., git rm is used. Not only it deletes but also remove files from the staging index and the working directory. If you wish then it could also delete files from the filesystem.
Deleting a file from the actual Git repository is a separate task that is done easily by the git rm command. But removing the file from the filesystem can be made in several other applications, e.g. a text editor, IDE, or file browser.
Also Check: How To Delete a GitHub Repository
Delete Files using git rm
The easiest way to delete a file in your Git repository is to execute the “git rm” command and specify the file to be deleted.
$ git rm <file> $ git commit -m "Deleted the file from the git repository" $ git push
Note that by using the “git rm” command, the file will also be deleted from the filesystem.
Also, you will have to commit your changes, “git rm” does not remove the file from the Git index unless you commit it.
As always, let’s have a quick example in order to illustrate the commands we just described.
- How to Remove Files from Git Commit | Git Remove File from Commit Stage
- How To Clear Git Cache | Learn Git Clear Cache in Different Ways
- How To Add and Update Git Submodules | Definition of Submodule
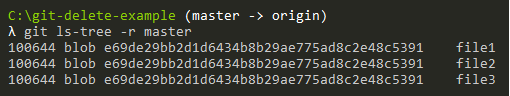
In my current repository, I have three files named “file1”, “file2” and “file3” and I want to delete the “file1” file from my Git repository.
By using the “git ls-tree” command, I am able to see the files tracked on my current branch.
$ git ls-tree -r master
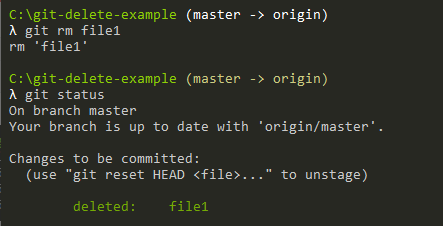
In order to delete the file “file1” from the Git repository and from the filesystem, we are going to execute the “git rm” command with the name of the file.
$ git rm file1 rm 'file1'
You should get a small confirmation message saying that the “rm” command was executed on this file.
So what happened here?
As you can see, by executing the “git rm” command, a “deleted” action was added to the changes to be committed.
It means that the file was removed from the filesystem but it was not deleted from the index just yet.
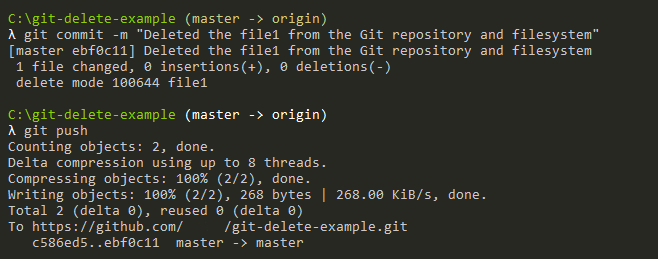
In order for the changes to be effective, you will have to commit your changes and push them to your remote repository.
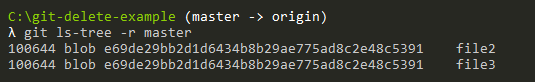
Now the file should be deleted from the filesystem and from the index, you can verify it by re-executing the “git ls-tree” command in order to list files in the current index.
Congratulations, you successfully deleted a file from your Git repository.
Removing Multiple Files
Deleting multiple files from a repo is the same as the early use-case of removing a single file using git rm. On the basis of your preferred method, there are some ways to do this. For instance, you can just explicitly list all files to be deleted like below:
$ git rm lib/db.js lib/api.js rm 'lib/api.js' rm 'lib/db.js'
Or, if there are more files than you feel like listing, you can always use the wildcard character:
$ git rm lib/*.js rm 'lib/api.js' rm 'lib/db.js'
Be noted that by deleting all of the contents from the lib directory, Git will also remove the actual directory itself. This is done because Git only tracks files, not directories:
$ git ls-files .gitignore index.js package.json
Delete Files Recursively on Git
In order to delete files recursively on Git, you have to use the “git rm” command with the “-r” option for recursive and specify the list of files to be deleted.
$ git rm -r <folder> $ git commit -m "Deleted the folder from the repository" $ git push
This is particularly handy when you need to delete an entire directory or a subset of files inside a directory.
As an example, let’s say that our Git repository has a folder named “folder1” that contains two files.
In order to delete this folder, and the files contained in it, we are going to execute the “git rm” command with the “-r” option.
$ git rm -r folder1
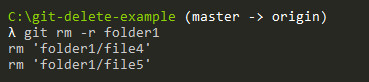
Again, do not forget that the changes are effective when you commit them, not before.
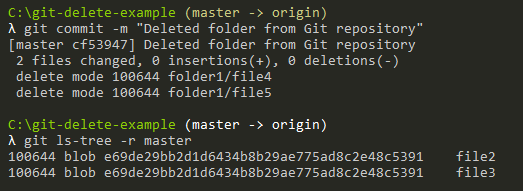
Congratulations, you successfully removed an entire folder from your Git repository.
Delete Files From Git Repository Only
In some cases, you want to delete files from the Git repository but not from the filesystem, you have to execute the “git rm” command with the “–cached” option.
$ git rm --cached <file> $ git commit -m "Deleted file from repository only" $ git push
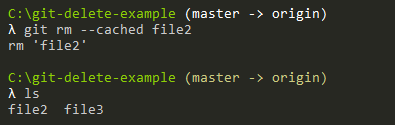
Back to our example, we currently have two files sitting in our working folder: file2 and file3.
Let’s pretend that we want to delete the file “file2” from the repository but we want to keep it on the filesystem.
To achieve that, we simply execute the “git rm” command with the “–cached” option.
$ git rm --cached file2
As you can see, after executing the “git rm” command, the file is still on the filesystem.
Awesome, you simply have to commit and push the changes now for them to be effective.
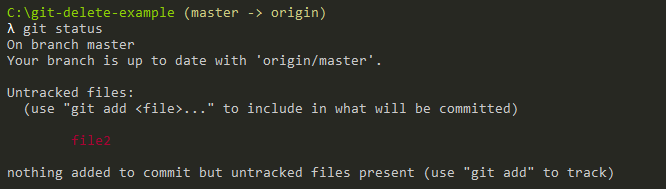
What’s in my git status?
Before committing your changes, you may notice with a “git status” command that the file was added to the changes to be committed, as well as in the list of untracked files.
Quite logic because your file is not tracked anymore as the result of your previous deletion.
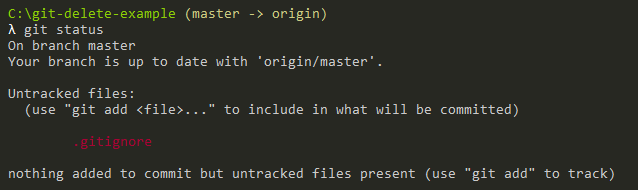
Now for the file not to be listed in your Git repository under the “untracked files”, make sure to add it to your Git Ignore file.
$ touch .gitignore # Content of the gitignore file file2
Commit your gitignore file and you should be good to go!
Delete Files From Git History
In some cases, you want to delete files from your entire Git history.
It may be the case for example if you committed a file that contains passwords or some sensitive information, that you want to remove.
In order to delete the file from Git history, you have to use the “git filter-branch” command and specify the command to be executed on all the branches of your Git history.
Finally, you want to specify the revision to execute the changes from we are going to choose HEAD (as a reminder, HEAD is the last commit of your repository).
In this case, the Git command to be executed is the “git rm” command we described earlier.
$ git filter-branch --force --index-filter --prune-empty "git rm --cached --ignore-unmatch <path_to_file>" HEAD
As the command is quite complex, let’s have a breakdown of all the options used :
- –force: quite self-explanatory, it forces the filter-branch to start even if it may not want to (given the documentation because it can contain temporary directories)
- –index-filter: option used in order to rewrite the index, exactly what we want in the case of a file deletion
- “git rm” command: the command to be executed on all branches, revisions, and commits matching in the history, in this case, it will remove the file from the repository and ignore files that don’t match
- –prune-empty: avoid having empty commits in the repository with zero files, this option will prune commits automatically
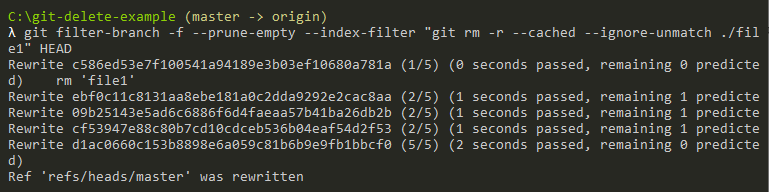
In this case, let’s say that we want to delete the file “file1” contained in our repository.
We are going to execute the following command.
$ git filter-branch -f --prune-empty --index-filter "git rm -r --cached --ignore-unmatch ./file1" HEAD
This command can take a while if your history contains many files, but in the end, the deleted file won’t be in your Git history anymore.
You can check with a “git log” command, but the commits linked to the deleted file should be pruned if necessary.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how you can easily delete a file from a Git repository, whether you want to delete it from the filesystem or not. Also, learned that it is completely possible to delete a file from an entire Git repository using the “filter-branch”.
Deleting files in Git is associated to file restoration, as a result, you may be interested in the following resources:
- How To Git Reset to HEAD
- How To Undo Last Git Commit
- How To Remove Files From Git Commit